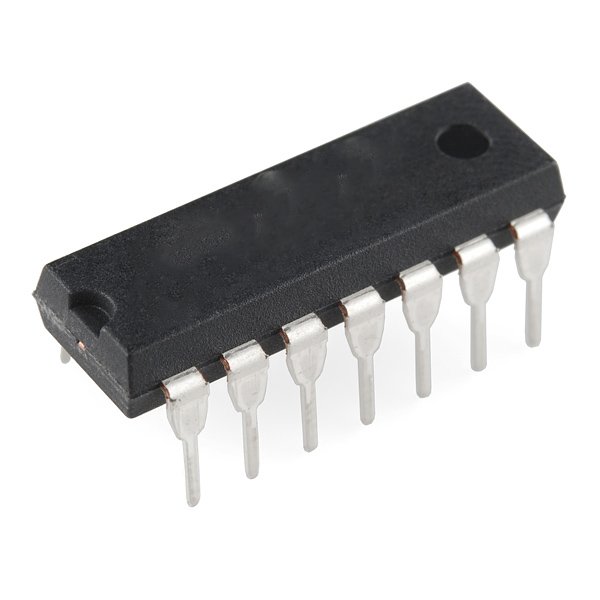
4013 IC Dual D-Type Flip-Flop CMOS
The CD4013BE integrates two D-type flip-flops in a single 14-pin DIP package, providing precise and reliable edge-triggered logic control for digital systems. Each flip-flop includes independent Data (D), Clock (CLK), Set (S), Reset (R), and Q/Q̅ outputs, enabling you to build synchronized latching operations with minimal external components.
You can use this IC to store logic states, divide frequencies, build binary counters, and create toggling circuits in both simple and complex systems. The CMOS architecture ensures ultra-low power consumption and broad compatibility with TTL and CMOS logic families.
Key Features
Dual D-type flip-flops in one IC
Edge-triggered with Set and Reset inputs
Individual Clock, D, Set, Reset, Q, and Q̅ for each flip-flop
Operates from 3V to 15V
High noise immunity and low power consumption
TTL and CMOS compatible logic levels
DIP-14 through-hole package
Operating temperature: -55°C to +125°C
Pin Configuration (DIP-14)
| Pin | Label | Description |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Q1 | Output of flip-flop 1 |
| 2 | Q̅1 | Inverted output of flip-flop 1 |
| 3 | CLK1 | Clock input for flip-flop 1 |
| 4 | R1 | Reset input for flip-flop 1 |
| 5 | D1 | Data input for flip-flop 1 |
| 6 | S1 | Set input for flip-flop 1 |
| 7 | GND | Ground |
| 8 | S2 | Set input for flip-flop 2 |
| 9 | D2 | Data input for flip-flop 2 |
| 10 | R2 | Reset input for flip-flop 2 |
| 11 | CLK2 | Clock input for flip-flop 2 |
| 12 | Q̅2 | Inverted output of flip-flop 2 |
| 13 | Q2 | Output of flip-flop 2 |
| 14 | VDD | Power supply (+V) |
Product Specifications
| Parameter | Value |
|---|---|
| IC Type | Dual D-Type Flip-Flop |
| Part Number | CD4013BE |
| Logic Family | CMOS |
| Package Type | DIP-14 ‘ |
| Supply Voltage | 3V to 15V |
| Max Clock Frequency | ~5 MHz (at 5V) |
| Logic Compatibility | TTL and CMOS |
| Output Current | ±1.0 mA |
| Operating Temp Range | -55°C to +125°C |
Typical Applications
Binary counters
Toggle switches
Frequency dividers
Latch and memory circuits
Timing and pulse generation
Edge detection circuits
Debouncing mechanical switches